Pomegranates, with their vibrant crimson hue and sparkling arils, have long been symbols of fertility, life, and abundance across countless cultures. You can even explore the delicate beauty of the Pomegranate flower , which represents the beginning of this fruit’s fascinating journey. But have you ever truly wondered about the journey of this magnificent fruit? Where do they come from? And what are the ideal conditions that allow them to flourish? As a passionate pomegranate enthusiast and a natural food expert with two decades of experience, let me take you on a world tour to discover precisely where do pomegranates grow, and why certain regions are simply the best for cultivating this ruby red jewel.
Table of Contents
Whether you’re curious where pomegranate trees grow in the United States or Europe, or looking for a map of their natural habitat, you’ll find all the answers you need right here.
Pomegranate Origins: Where Did It All Begin? (Where Do Pomegranates Come From?)
The homeland of the pomegranate, scientifically known as Punica granatum, is believed to be a region stretching from modern-day Iran (ancient Persia) to northern India. This area served as the “cradle” of the pomegranate, from which its cultivation gradually spread along ancient trade routes to the Mediterranean basin, North Africa, and Central Asia.
According to research from Harvard University’s Nutrition Source, pomegranates have been cultivated for thousands of years in these regions due to their resilience and adaptability to semi-arid climates.
Ideal Growing Conditions: What Does a Pomegranate Tree Love? (Pomegranate Trees Care & How Does Pomegranate Grow?)
To truly understand where pomegranate trees grow best, you need to grasp the conditions they thrive in. Pomegranate trees are resilient and adaptable, but they truly flourish in:
Warm, Dry Climates
Pomegranate trees prefer hot, dry summers and relatively cool (but not severely cold) winters. High temperatures during the growing season are crucial for developing their rich, sweet flavor and vibrant fruit color.
Full Sun Exposure
These trees need at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily to grow robustly and produce good fruit.
Well-Draining Soil
While they can adapt to a wide range of soil types, they prefer well-draining sandy loam. They do not tolerate waterlogged soil.
Drought Tolerance
Once established, pomegranate trees are highly drought-tolerant, making them suitable for semi-arid regions. However, regular watering during fruit development improves their size and juiciness.
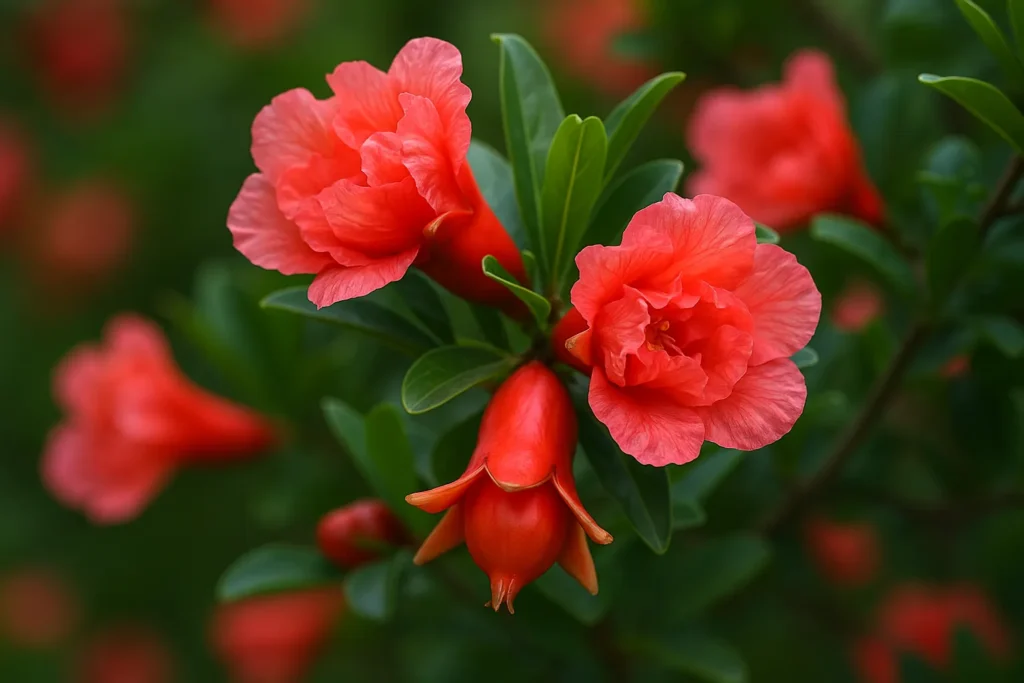

Interestingly, this tree is valued not only for its fruit but also for the beauty of the pomegranate flower that blooms before the fruit appears! These flowers themselves hold benefits and beauty worthy of their own dedicated article, but for now, let’s focus on the fruit’s journey.
Where Do Pomegranates Grow Naturally & Commercially? A Global Look
Today, pomegranate orchards can be found in many parts of the world, but some regions stand out for their quality and prolific production.
1. The Middle East and North Africa (Where Are Pomegranates From?)
This region remains the heartland of pomegranate cultivation:
- Iran: Considered one of the largest producers and exporters of pomegranates globally, renowned for its diverse varieties and rich flavors.
- Turkey: Produces significant quantities and exports pomegranates to Europe.
- Egypt, Lebanon, Syria: Pomegranates are widely grown for local consumption and export.
2. The United States (Where Do Pomegranates Grow in the United States?)
- California: The leading state for pomegranate cultivation in the U.S. The hot, dry climate of California’s Central Valley is perfect for varieties like ‘Wonderful’, which make up the majority of commercial production.
- Arizona and Texas: Also cultivate pomegranates, but in smaller quantities compared to California.
3. Europe (Where Do Pomegranates Grow in Europe?)
- Spain: One of Europe’s most important pomegranate producers, especially the Valencia and Granada regions. Spanish pomegranates are known for their high quality.
- Italy, Greece, Cyprus: Benefit from the suitable Mediterranean climate to grow pomegranates both commercially and for local markets.
4. Asia (How Fast Do Pomegranate Trees Grow?)
- India: A major producer of pomegranates, particularly the ‘Bhagwa’ and ‘Ganesh’ varieties, known for their sweetness and dark color.
- China: Cultivates pomegranates on a large scale in several regions.
- Afghanistan and Uzbekistan: Produce high-quality pomegranates in their historical growing areas.
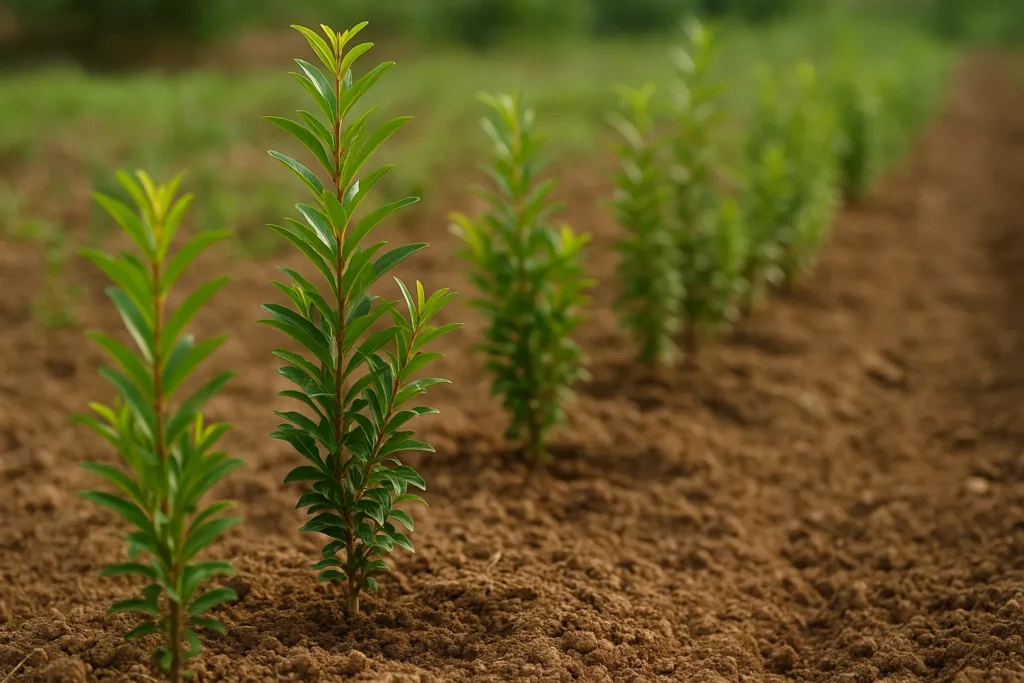

How fast do pomegranate trees grow?
Pomegranate trees are relatively fast-growing. They can start bearing fruit within 2-3 years of planting and reach peak production after 5-7 years. This rapid growth is one reason for their significant popularity in commercial agriculture.
Why Are Pomegranates Important? Deep Symbolism and Value (Pomegranate Symbolism & Pomegranate Family)
Pomegranates are more than just a fruit; they also carry profound pomegranate symbolism and cultural significance in many civilizations:
- Fertility and Abundance: Due to their numerous seeds and abundant juice.
- Life and Immortality: In ancient Egyptian art.
- Justice and Hope: In Christian and Jewish traditions.
Pomegranates belong to the Punicaceae family, which was formerly a distinct family but is now subsumed within the Lythraceae family. This family includes other well-known plants such as henna, highlighting the evolutionary relationships within the plant kingdom.
Pomegranates: Are They an Expensive Fruit? (Why Is Pomegranate So Expensive?)
You might sometimes wonder why pomegranate is so expensive, especially out of season. Several factors contribute to its price:
- Manual Harvesting: Pomegranate harvesting is often done by hand to avoid damaging the fruit, which increases labor costs.
- Storage and Transportation: While pomegranates store and transport well, the costs of shipping them from producing regions to distant markets add to the final price.
- Increasing Demand: With growing awareness of its health benefits, global demand for pomegranates is rising.
- Complexity of Preparation: Deseeding pomegranates can be time-consuming, making ready-to-eat products (like packaged arils or juice) higher in price.
Which Country Has the Best Pomegranates?
Claiming one country has the “best” pomegranates is challenging, as “best” often depends on personal taste and specific varieties. However, certain countries are renowned for producing exceptional pomegranates:
- Iran: Known for its diverse and richly flavored varieties, some sweet-tart, others intensely sweet.
- India: Famous for varieties like ‘Bhagwa’ and ‘Ganesh’, noted for their deep red color, soft seeds, and sweetness.
- Spain: Produces varieties with a balanced flavor profile, popular throughout Europe.
- California (USA): Known for the ‘Wonderful’ variety, characterized by its large size, deep red color, and tart-sweet tang.
Each region offers something unique for pomegranate lovers around the globe.
From Origin to Your Table
We’ve journeyed across the globe, discovering where pomegranates grow, from their ancient homeland in Persia to the sunny orchards of California and the fertile fields of India. This fruit isn’t just a beautiful addition to your plate; it’s the result of ideal climatic conditions and cultivation spanning generations.
Whether you’re enjoying its refreshing juice or adding its glistening arils to your salad, you’re tasting a piece of rich natural and agricultural history. Don’t hesitate to explore this ruby red gem and savor its myriad benefits!


